Kinematics
Introduction
Movement is an essential component of your FTC Robot and Pod provides a set of classes and helpers through the Kinematics package for you to streamline movement operations on your robot.
These include robot tele-operated and autonomous movement, and actuators movement, for both linear and angular actuators.
Robot Movement
For a more in depth understanding of robot kinematics, we recommend reading Game Manual 0 - Kinematics guide.
Classes:
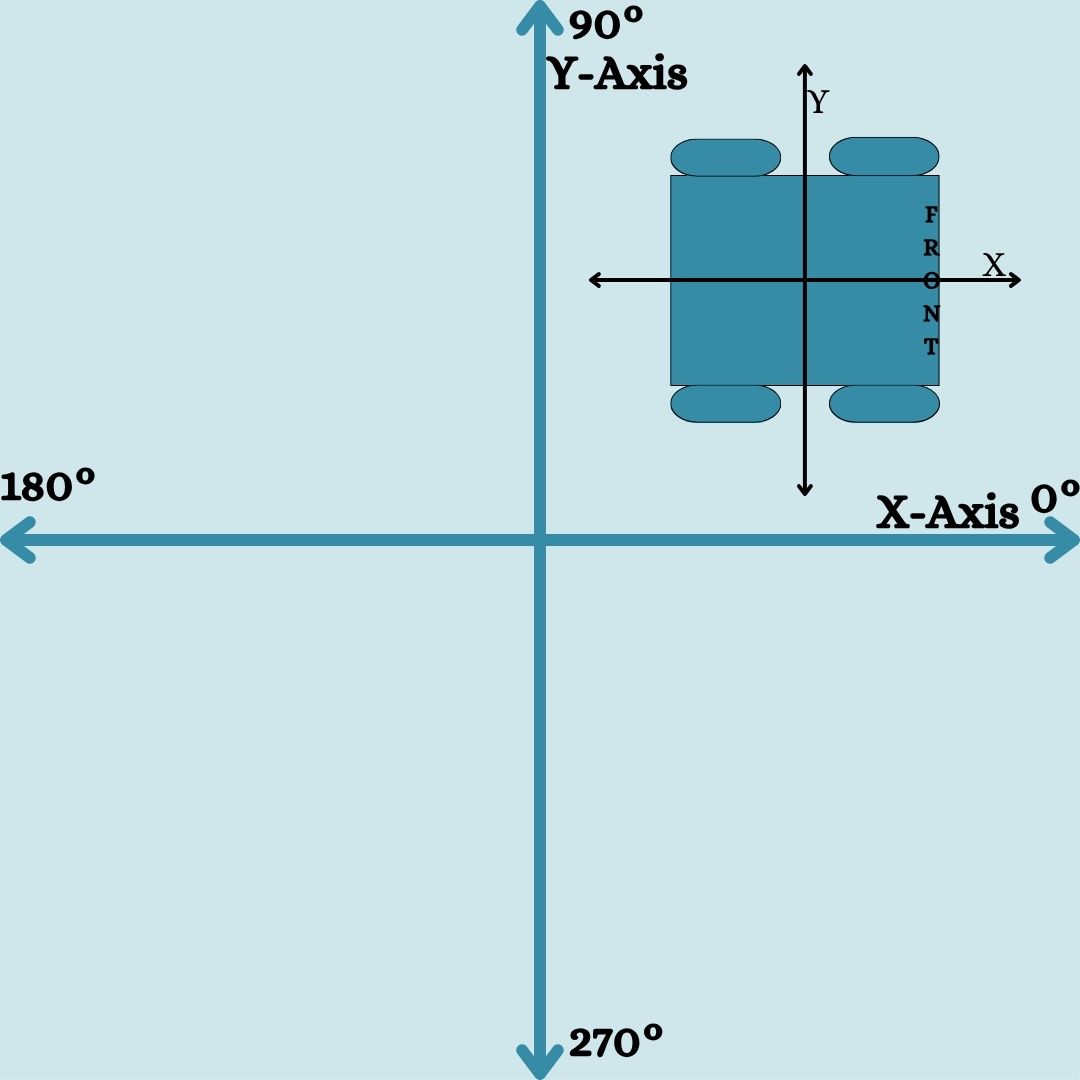
Field Orientation
Before anything, it is important to align on a the robot and field orientation, as the robot movement is relative to field position:
Dead Wheel Kinematics
Provides an accurate field-relative localization using three unpowered encoded wheels (dead wheels) by comparing encoder delta’s over time.
update takes the integer positions of the left, right, and center dead wheel to calculate the new robot position on the field.
updateAndReset takes the integer positions of the dead wheels as well as a pose to set the robots current position to the current one and the velocity to zero.
Mecanum Forward Kinematics
Provides field-relative localization using encoded mecanum wheels. This method is prone to slippage issues but it can be used by teams who do not posses dead-wheels on the robot.
Mecanum Inverse Kinematics
Calculates motor actuation based on intended direction of movement (from gamepad or autonomous holonomic controller).
Actuator Movement
The following classes help with actuator movement. Linear actuators cause a linear motion on the robot, given and power input. Angular actuators cause a circular motion on the robot, given a power input.
Classes:
Linear Actuator Calculator
Convert pulses to linear distance (in in chosen units) and vice versa, given the parameters of the gear-ratio’s and wheel diameters. It can be used in Linear slides or any other type of linear motion.
Angular Actuator Calculator
Convert pulses to angular rotation (in radians) and vice versa, given the parameters of the gear-ratio’s. Deals with angular motion/rotation. This type of motion refers to rotating arms, joints, and etc.